This means that companies with larger amounts of current assets will more easily be able to pay off current liabilities when they become due without having to sell off long-term, revenue generating assets. On December 31, 2016, the balance sheet of Marshal company shows the total current assets of $1,100,000 and the total current liabilities of $400,000. The current ratio is a liquidity measurement used to track how well a company may be able to meet its short-term debt obligations. Measurements less than 1.0 indicate a company’s potential inability to use current resources to fund short-term obligations.
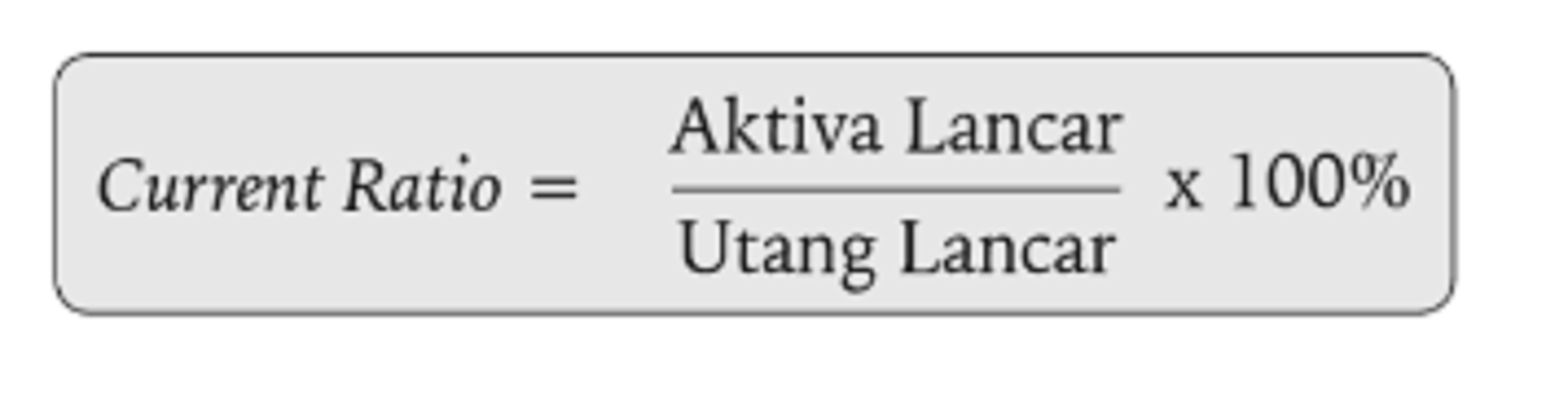
How Do You Calculate the Current Ratio?
The range used to gauge the financial health of a company using the current ratio metric varies on the specific industry. For the last step, we’ll divide the current assets by the current liabilities. Companies with shorter operating cycles, such as retail stores, can survive with a lower current ratio than, say for example, a ship-building company. The current ratio should be compared with standards — which are often based on past performance, industry leaders, and industry average. The current ratio also sheds light on the overall debt burden of the company.
Table of Contents
Company A also has fewer wages payable, which is the liability most likely to be paid in the short term. Current liabilities are obligations that are due to be paid within one year. Examples of current liabilities include accounts payable, short-term loans, and wages payable. The current ratio accounts for vertical analysis common size analysis explained all of a company’s assets, whereas the quick ratio only counts a company’s most liquid assets. However, when evaluating a company’s liquidity, the current ratio alone doesn’t determine whether it’s a good investment or not. It’s therefore important to consider other financial ratios in your analysis.
How do you calculate the current ratio?
As with many other financial metrics, the ideal current ratio will vary depending on the industry, operating model, and business processes of the company in question. A high current ratio, on the other hand, may indicate inefficient use of assets, or a company that’s hanging on to excess cash instead of reinvesting it in growing the business. Here, we’ll go over how to calculate the current ratio and how it compares to some other financial ratios. However, if you learned this skill through other means, such as coursework or on your own, your cover letter is a great place to go into more detail.
If you get 1.0 exactly, that means the assets are exactly the same as liabilities, which is essentially financial balance, as far as this metric is concerned. Companies with a healthy current ratio are often viewed as being more creditworthy and better able to meet their short-term obligations. There are no specific regulatory requirements for the value of the current ratio in the US or EU.
Accounting Services
This is because it could mean that the company maintains an excessive cash balance or has over-invested in receivables and inventories. By contrast, in the case of Company Y, 75% of the current assets are made up of these two liquid resources. The current ratio is one of the oldest ratios used in liquidity analysis. The volume and frequency of trading activities have high impact on the entities’ working capital position and hence on their current ratio number. Many entities have varying trading activities throughout the year due to the nature of industry they belong.
This is important if you want to buy stock in a company that’s solvent and will remain that way for the long term. Seasonal businesses can experience substantial fluctuations in their current ratio. This figure can be interpreted through the lens of where a company is in its operating cycle. A current ratio above 1 signifies that a company has more assets than liabilities. The current ratio may not be particularly helpful in evaluating companies across different industries, but it might be a more effective tool in analyzing businesses within the same industry.
Public companies don’t report their current ratio, though all the information needed to calculate the ratio is contained in the company’s financial statements. One of the biggest fears of a small business owner is running out of cash. To know whether a company is truly on the cusp of hitting a $0 balance in their accounts, you can’t simply look at the income statement.
What counts as a good current ratio will depend on the company’s industry and historical performance. Current ratios over 1.00 indicate that a company’s current assets are greater than its current liabilities, meaning it could more easily pay of short-term debts. A current ratio of 1.50 or greater would generally indicate ample liquidity.

Current assets are assets that are expected to be converted into cash or used to pay off short-term obligations within one year. Examples of current assets include cash, accounts receivable, marketable securities, and inventory. The current ratio is balance-sheet financial performance measure of company liquidity.
- Small business owners should keep an eye on this ratio for their own company, and investors may find it useful to compare the current ratios of companies when considering which stocks to buy.
- In other words, the current ratio is a good indicator of your company’s ability to cover all of your pressing debt obligations with the cash and short-term assets you have on hand.
- Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.
For example, a current ratio of 4 means the company could technically pay off its current liabilities four times over. Generally speaking, having a ratio between 1 and 3 is ideal, but certain industries or business models may operate perfectly fine with lower ratios. Putting the above together, the total current assets and total current liabilities each add up to $125m, so the current ratio is 1.0x as expected. The above analysis reveals that the two companies might actually have different liquidity positions even if both have the same current ratio number. While determining a company’s real short-term debt paying ability, an analyst should therefore not only focus on the current ratio figure but also consider the composition of current assets. In this example, Company A has much more inventory than Company B, which will be harder to turn into cash in the short term.